Filament Winding
What is Filament Winding
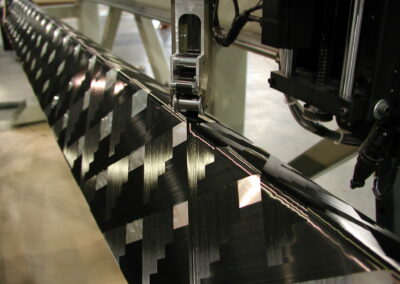
Filament winding is best used to manufacture tubular components or tanks with a constant axis of rotation. First, a mandrel is installed into the machine. Fiber tows are routed through a fiber delivery system on the filament winding machine and then attached to the mandrel. The mandrel rotates while the fiber delivery eye moves to predetermined positions to create repeating geometric patterns. Fiber reinforcement is applied in layers, typically at an orientation anywhere between 90 degrees (hoop) and ~10 degrees in relation to the axis of the part.
Key Benefits of Filament Winding
- Affordability: The automated process of filament winding is a cost-effective way to produce components with qualifying geometric and structural requirements.
- Repeatability: Key process parameters such as fiber tension and resin content may be controlled to produce components with a low degree of variability.
- Flexibility: The various layers of material may be adjusted to match the desired structural requirements of the component load case. Reinforcement may also be applied supplementary by hand or roll wrapping to achieve a true zero-degree ply, or even for localized reinforcement.
As a leader in numerical-controlled filament winding, Nammo Composite Solutions’ custom-made equipment is designed with accuracy, reliability, and rate production in mind. The company currently runs a combination of six single-spindle and multi-spindle machines that support production and the engineering of new designs and applications. Nammo Composite Solutions’ filament winding machines are flexible and facilitate both wet-wound and towpreg materials, including carbon fiber, fiberglass, and aramids. The machines typically accommodate components up to 24 inches in diameter and up to 20 feet in length, though larger diameter parts may be produced with modifications to equipment. The winding eyes on the machines have multiple degrees of freedom to accommodate complex geometry turnarounds at the ends of the part.